Diamond Education
Buying a Diamond: Everything To Know About the 4 C's.
Buying a diamond signifies an important moment in your life, and we understand that for many it can also be a bit of an intimidating experience. For most people, buying an engagement ring is the first, most important purchase to date. At Firenze Jewels, we want this experience to be an enjoyable, satisfying one for you. Our friendly, knowledgeable team is on hand to provide you with all the information you will need. On staff we have a team of GIA certified gemologists, eager to share their expertise with you. We are pleased to guide you throughout this process.
For your convenience, we have gathered some of the basic, general concepts (a.k.a. the 4 C's) that you should become familiar with as you start looking for a diamond. We strongly feel that an educated consumer will be a satisfied client. Please take your time and read this at your leisure. While this is a great place to start, remember, we are always here to assist you.
COLOR
Normal color range diamonds (what most people consider 'white' diamonds) are graded by their relative lack of color. A diamond that is 'whiter' has little or no visible coloration. Diamonds with less color are considered more desirable and have a higher value.
Below is a chart illustrating how diamonds are graded according to color by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA).The difference in color between one letter grade to the next is quite small. It usually takes a well trained eye and years of experience to color grade a diamond.
Truly colorless diamonds are actually quite rare. Most diamonds used in jewelry are nearly colorless, and fall in the normal color range.
It is important to distinguish the normal range 'white' diamonds from 'fancy' color diamonds. Diamonds actually range in color from faint yellow or brown to very rare pinks, blues, greens, and other colors known as "fancies".
To summarize,
D-F: Colorless: perfect or almost perfect color.
G-J: Near colorless: good to very good color.
K-M: Light but noticeable yellow or brown tint.

CLARITY
Diamonds have unique birthmarks or natural inclusions (found internally, though some may break the surface of the stone), and blemishes which include scratches and nicks on the diamond's surface. Clarity refers to the relative absence of inclusions and blemishes. A diamond's clarity is determined by using a 10X magnifying glass and a trained eye.
Below is a list of the clarity grades. Moving from one grade to the next can greatly influence the overall value of a diamond. Diamonds that have fewer inclusions are rarer, and therefore more valuable.
Flawless - No inclusions or blemishes under 10X magnification.
Internally Flawless - No inclusions viewed under 10X magnification, but has some minor blemishes.
VVS1 & VVS2 - Very, Very Slightly Included: Very difficult to see the minute inclusions under 10X magnification.
VS1 & VS2 - Very Slightly Included: Inclusions are not visible to the unaided eye. Tiny inclusions (small clouds, crystals, or feathers) are visible with 10X magnification.
SI1 & SI2 - Slightly Included: Contains inclusions (clouds, included crystals, knots, cavities, & feathers) that are visible under 10X magnification.
SI3 - Slightly Included-EGL: SI3 is an EGL grade and is not recognized by GIA or other gemological institutions. It may be graded by GIA as either SI2 or I1. SI3 diamonds do not have any black inclusions or cracks visible to the naked eye, but may have some very minor white inclusions that can be seen with the naked eye.
I1, I2, I3 - Included: Inclusions that are obvious under 10X magnification, and visible to the naked eye.
CARAT WEIGHT
Diamonds are weighed in units of a metric carat (ct). One metric carat is just over .007 ounce. One ounce is equal to almost 142 carats. When a diamond weighs over a carat, the weight is expressed in carats and decimals, rounded to the nearest hundredth of a point (i.e. 1.52 ct).
One important point to keep in mind when considering the carat weight of a diamond is to know that the 'per carat' price increase significantly as a diamond gets larger. For example, we know that all things held equal (same cut, color, clarity) larger stones are worth more than smaller ones. However, many people don't realize that a 2.00 carat diamond is worth more than just twice as much as a 1.00 carat diamond. This is because larger diamonds are rarer than smaller diamonds. The more scarce the diamond is, the more it is worth.
Carat weight is an obvious factor in determining the value of a diamond. However, two diamonds of equal carat weight can have very different prices, depending on their quality.
CUT
Many people confuse cut with the shape (i.e. round, princess, oval) of a diamond. The shape of the diamond is mainly a matter of personal preference and does not directly affect the value. Cut refers to the proportions and finish of a diamond. Cut is what enables a diamond to make the best use of light. It is the work of a master cutter that allows the diamond to be cut in such a way as to permit the maximum amount of light to be reflected through the diamond.
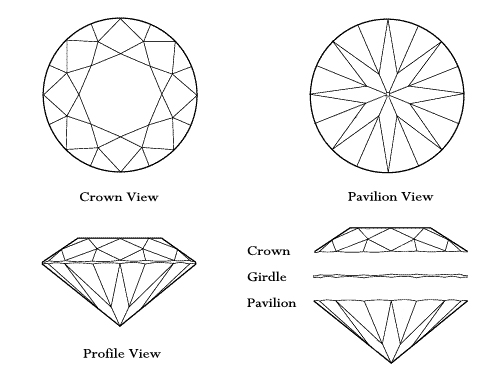
The three important concepts to keep in mind with cut are: proportion, symmetry, and finish of the diamond. The proportions are the size and angle relationships between the facets and different parts of the stone. Finish includes polish and details of facet shape and placement. When the proportion, symmetry, and finish of a diamond are good, you will notice that the diamond is brilliant, sparkly, and full of 'fire' or scintillation.
The three main parts of a diamond are: the crown, the girdle, and the pavilion. The large flat surface on the top of the diamond is called the table. Diamonds may also have a very tiny flat facet at the bottom of the pavilion called the culet. A typical round brilliant cut diamond has 58 tiny facets, each carefully cut and sharply defined.
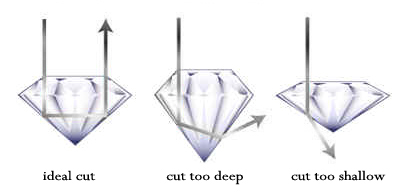
A skilled cutter will try to produce the maximum return of light by considering the table size, crown angle, and pavilion depth. Pavilion depth refers to the distance from the top of the girdle to the culet. A pavilion that is too shallow or too deep will permit light to escape from the side or the bottom of the diamond. When a diamond is cut well, the light will refract from one facet to another and disperse back through the crown or top of the stone.
SUMMARY
To conclude, there are 4 major factors to consider when buying a diamond: carat weight, cut, clarity, and color. No single factor is necessarily more important than the others. When assessing the true value of a diamond, all 4 factors are should be considered collectively.
We encourage you to contact us with any questions you may have. We have an extensive collection of loose diamonds, including G.I.A. and E.G.L. certified stones. Because of the large volume of stones that we sell, we are able to offer you quality diamonds at affordable prices.
*A NOTE ON CLARITY ENHANCED OR COLOR TREATED DIAMONDS:
We NEVER sell clarity enhanced or color treated diamonds. At Firenze Jewels, you can be certain that you will only purchase a 100% natural diamond that has never been artificially treated in any way.
*A NOTE ON CONFLICT DIAMONDS:
Conflict diamonds are diamonds that originate from areas controlled by forces or factions opposed to legitimate and internationally recognized governments, and are used to fund military action in opposition to those governments, or in contravention of the decisions of the Security Council.
Today, there is an international monitoring system called the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) in place, which was created to certify the origin of rough diamonds from sources known to be conflict-free. A well-structured 'Certificate of Origin' regime can be an effective way of ensuring that only legitimate diamonds (those from government-controlled areas) reach the market. Additional controls by Member States and the diamond industry are needed to ensure that such a regime is effective. Today, independent auditing systems are charged with ensuring compliance with KPCS, by tracking diamonds from their place of origin to delivery. The Patriot Act requires that every diamond dealer in the United Sates maintain compliance with KPCS.
Firenze Jewels, Inc. is deeply committed to selling only legitimate diamonds. We have vowed not to deal with or purchase from any source that deals in conflict diamonds. We fully support the Kimberly Process Certification Scheme and work closely with only the most reputable, professional diamond to ensure compliance.




















